-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
What You Must Know When Developing an mHealth App
Nowadays, patients have a number of opportunities to get cheaper and faster diagnosis and treatment thanks to modern technologies. Mobile health technologies are improving healthcare services. In this article, we take a look at the current state of the mHealth market and find out the opportunities for mHealth app development.
What is mHealth?
Mobile health (or mHealth) is the integration of mobile technology in healthcare. mHealth apps enhance communication between patients and doctors, monitor chronic diseases, provide quick access to medical data, and more. These apps make healthcare services more accessible and significantly improve the patient experience.

The global mobile health industry is expected to reach a market size of almost $60 billion by 2020. Key factors that have an impact on the mHealth market include widespread use of mobile devices and rapid advances in mobile technologies.
What types of mHealth apps are there?
mHealth apps are used by both patients and doctors. The technology provides opportunities for monitoring health, keeping health-related data, managing chronic conditions, and getting online consultations. mHealth also includes fitness and wellness apps. Let’s take a closer look at types and uses of mHealth apps.
Telemedicine apps
Telemedicine lets patients get consultations without having to visit a doctor’s office. In fact, almost 75 percent of all doctor, urgent care, and ER visits are either unnecessary or could be handled effectively over the phone or by video. Telemedicine apps make healthcare services more convenient and accessible for patients, letting them receive medical care from healthcare providers via mobile devices. Patients can save time and money using telemedicine while getting a better patient experience.

The Amwell app lets patients communicate with experienced doctors through video and messaging. It gives 24-hour access to medical care, which is a big advantage in case of urgent matters. Amwell users can see what doctors are available at the moment and choose one. The company claims that the average time a patient has to wait for an online visit is just two to three minutes.
Personal health record apps
According to Deloitte, 74 percent of patients have to provide the same information to multiple healthcare professionals. Having access to shared health-related data, doctors can focus more on patient care.
Personal health record apps let users store and manage their health-related data, share it with their doctors, and access electronic health records (EHRs). All of this can be done on the go with the help of mobile devices.
Capzule PHR is an example of a personal health record app that allows patients to store, access, and manage health-related data as well as share it with physicians. Capzule users can also add family members and manage their health records. Additional features of Capzule PHR include calendar reminders and data visualization.
Apple’s Health app lets users store and view their medical information, including medications and lab results, on their iPhones. The health records section lets users add healthcare providers to the app to see medical data without logging into providers’ websites. Patient’s health-related data is stored in one place, making it faster and more convenient to access.

Apps for remote health monitoring
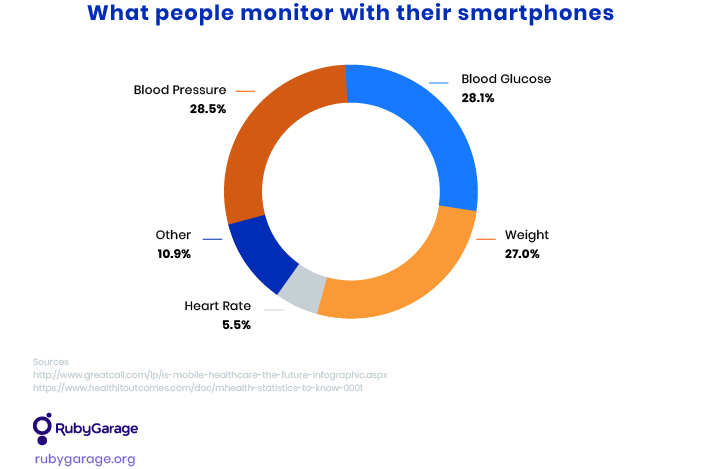
Remote health monitoring apps are mostly used to manage chronic conditions like diabetes. Most of these apps can link to devices that track blood glucose, weight, and other health metrics. Using a health monitoring app, a doctor can keep an eye on their patients’ health conditions without visits to the office.
ChronicCareIQ offers an app that lets patients answer questions on their smartphones. Doctors can analyze data and monitor their patients’ conditions remotely.
Sixteen percent of apps developed for a specific disease are for managing diabetes. One of the most popular diabetes apps is Glucose Buddy Diabetes Tracker. This app lets users track their blood sugar, weight, and medications. The app also provides insights into health trends.
Apps for reminders and alerts
People not taking prescribed medications or taking them incorrectly is a common problem in healthcare. No wonder. People are so busy these days that it’s difficult to keep all their medications in mind. In fact, forgetfulness tops the list of reasons why patients don’t take prescribed meds.
Reminder apps can come in handy. With reminder apps, patients can be sure they won’t forget about important things like doctor appointments or medications.
The Pill & Med Reminder app by Medisafe sends users push notifications when it’s time to take medications. The app stores information about a patient’s dosage. Users can also see progress reports and share them with doctors.
Wellness apps
A growing number of people are interested in healthy lifestyles. The Patient Adoption of mHealth Report by IMS Institute shows that consumer mHealth apps targeting wellness (including fitness, lifestyle, and nutrition) account for two-thirds of all mHealth apps.
Wellness apps help users with exercise, nutrition, and activity tracking. These apps provide training programs and nutrition plans to help users reach their health goals. Most of these apps require a connection to a wearable device and apps like Health that allow users to store data from various devices and third-party apps in one place.
If you would like detailed information about this type of mHealth app, read our guide to fitness app development. There, you’ll find a list of fitness app features, real-life examples, and tips for developing a fitness app.
What are the challenges of developing an mHealth app?
The biggest challenges related to mHealth app development include privacy concerns and compliance with laws and regulations. Also, as the Deloitte 2016 Survey of US Health Care Consumers shows, consumers are worried that mobile health services may be of poor quality compared to in-person visits.

You may face several challenges when developing an mHealth app.
- Building trust. Even though mHealth apps can improve the healthcare system and the patient experience, there’s a lack of patient trust. Patients are mostly worried about the security of their medical information and the quality of healthcare services. These concerns result in a lack of trust. So filling the trust gap is crucial for the adoption of mHealth apps.
- Privacy and security. While digital transformation brings lots of benefits to various industries, it also makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks. To avoid breaches of medical and personal data, healthcare solutions need to focus more on tools and technologies that provide data security.

- Compliance with healthcare legislation. Different countries have their own regulations that protect personal health information. An mHealth app, just like any app handling sensitive data, must comply with laws of the countries where your app users live. In the US, for example, mHealth apps must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This act regulates how personal health information is collected, stored, and shared. That means that mHealth apps targeting the American market must be developed based on HIPAA rules.
What are the trends in mHealth?
Taking into account the challenges the industry is facing, mHealth solutions will focus on the patient experience, preventive care, and data security. Let’s take a look at the technology trends in mHealth.
Blockchain technology
Various industries are already adopting the blockchain, and healthcare is no exception. Applications of the blockchain in the healthcare market are predicted to be worth $5.5 million by 2026. The main advantage of the blockchain is that it can help to secure medical data and share it safely. With cybersecurity being an issue, the blockchain provides the ability to protect health-related data from breaches. However, unlocking the blockchain’s potential for healthcare won’t be a quick process. As CB Insights notes, it’s still early days for blockchain and healthcare applications.
Artificial Intelligence
Accenture research shows that healthcare ranks higher than all other industries in use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI provides several advantages for the healthcare industry. First, while mHealth apps and tracking devices can gather health-related data, AI can process and analyze huge amounts of such data. In the future, AI will enable mHealth apps to diagnose patients based on their medical data and symptoms. The technology is already used to help medical workers with monotonous tasks like managing health records. Large tech companies are showing interest in using AI to improve healthcare. For example, Google has announced that it’s absorbing DeepMind Health to turn DeepMind’s Streams app into “an AI-powered assistant for nurses and doctors.” The Streams app collects patients’ medical data and lets doctors review it. The AI health market is predicted to reach $6.6 billion by 2021.
The Internet of Medical Things
IoMT allows medical devices to connect and exchange health-related data. This technology gathers data from various tracking devices and lets doctors monitor their patients’ conditions remotely. These devices can measure blood pressure, heart rate, glucose level, and more. For example, the Apple Watch Series 4 can monitor a user’s heart rate and alert them if it’s higher or lower than usual. All this data is stored in the iPhone Health app. Frost & Sullivan forecasts the number of IoMT devices to grow to 20 to 30 billion by 2020, compared to 4.5 billion in 2015.
Want to know more about the latest technologies? Subscribe to our newsletter!










