-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
QA Testing Process from A to Z
Quality is generally transparent when present, but easily recognized in its absence.
Quality assurance is one of the key aspects of product development. It’s an inevitable part of a project and requires careful planning, preparation, and engagement. But do you know what QA testing process entails? In this post, we show you how the quality assurance process is built and what activities it includes so you’ll know exactly how a QA team tests your product.
Before we get into it, let’s find out if you really need a QA team on your project and what benefits such cooperation can bring.
What’s the purpose of QA testing process?
When developing a small project or building an MVP to verify a business idea, some startups believe quality checks performed by developers are enough. As a result, such teams get stuck in endless bug fixes with a product that’s impossible to maintain, support, or develop further.
QA testing performed by a team of professional quality assurance engineers is a must if you want to:
- reduce development costs. The cost of defects detected early is significantly lower than the cost of defects detected after the release. By incorporating QA activities at the early stages of product development, you can save up to 30 percent on bug fixes.
- simplify the development process. QA engineers who participate in development from the very beginning can positively influence important development decisions, foresee defects and bugs, and offer workable solutions to avoid them.
- create a flawless product. The main goal of a QA team is to help you create a seamlessly working product to provide your customers with the best possible user experience.
Now that you know why the result is worth the effort, let’s find out what a QA team’s workflow looks like.
How a QA team tests your product
This section is a detailed step-by-step description of how the quality assurance process is built at RubyGarage. This workflow is based on QA best practices and more than eight years of experience.
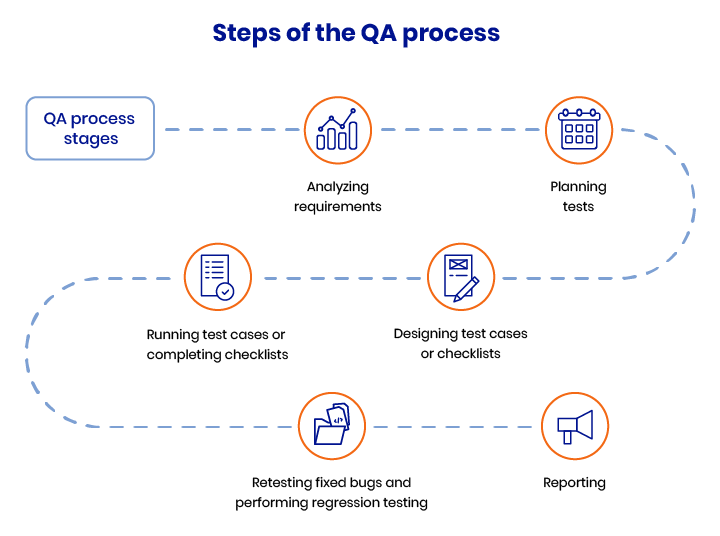
Step 1 — Analyzing requirements
Requirements elicitation is the process of researching and discovering functional and non-functional product requirements. During this step, quality assurance engineers review product specifications and product designs (if they already exist) and identify any problems with the requirements. This process allows a team to make sure all requirements are clear, traceable, and testable.
After gathering and analyzing requirements, a QA team should make a list of bugs or improvements related to those requirements.
Step 2 — Planning tests
A test plan is a document that a QA team creates in cooperation with the client and their development team. When creating a test plan, a quality assurance team determines the scope of testing, necessary resources, testing environments, testing objectives, main suspension and exit criteria, test deliverables, and a testing schedule.
A test plan is one of the main documents required for a successful QA testing process. It allows you to:
- make sure the final product satisfies your business needs. A test plan includes all product requirements and lists testing activities to be undertaken to ensure that the product meets all of those requirements.
- get better control over the testing process. The client and QA team should discuss all deliverables the team has to provide the client with and agree on communication channels and meeting frequency. Getting regular reports and holding frequent online meetings allows a client to keep up with the pace of their QA team and be aware of their current tasks.
- Establish realistic time frames. A QA team estimates the scope of work and includes it in a test plan along with the time frame, cost, and schedule of all testing activities.
Step 3 — Designing a test case or checklist
Once the scope of work and all requirements are clearly set, the QA team can proceed to designing test cases or checklists.
Test cases describe test inputs, execution conditions, and expected results for each test to check the functionality of a software product. Test cases allow quality assurance engineers to perform a sequence of steps to ensure that a software product is bug-free and that it works as it’s supposed to from the end user’s point of view.
A checklist is a simplified variation of test cases that covers all possible actions a user can take within a piece of functionality. In comparison to test cases, checklists are less time-consuming to create and implement.
Here’s an example of a checklist that the RubyGarage QA team created for one of our projects.
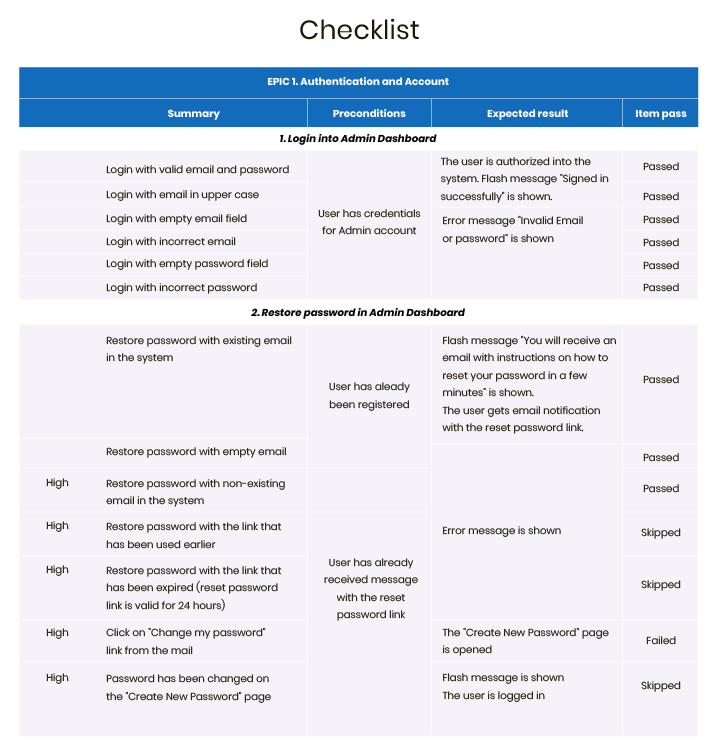
Checklists allow you to save time but are effective only for small teams and small projects, while test cases are more beneficial on larger projects with bigger teams.
Step 4 — Running test cases or completing checklists
When test cases or checklists are ready, QA engineers start checking functionality at the API and UI levels. Manual testers run test cases or go through checklists while automation testers use special frameworks like Selenium, Cucumber, RSpec, and Capybara to run automated test scripts.
While running test cases or completing checklists, quality assurance engineers add information about every bug and the conditions under which they were detected to a defect tracking system. This way developers can start fixing bugs as soon as possible.
Step 5 — Retesting fixed bugs and performing regression testing
When developers fix bugs, quality assurance engineers check all fixed defects one more time. Testers have to make sure a bug is fixed and that a particular piece of functionality works seamlessly.
Another check that QA testers perform during this phase is regression testing. Regression testing makes sure bug fixes haven’t caused new bugs or distortions in existing functionality.
At RubyGarage, we implement autotests to speed up regression testing and ensure product stability.
Step 6 — Reporting
After each development iteration, the QA team provides a test report with a list of all performed testing activities as well as final test results.
Regular reports allow clients to not only control the testing process but also get a better picture of the current product quality and make informed decisions about whether it’s time to release a product.
Recap
This effective workflow helps thee RubyGarage QA team build close and transparent cooperation with a client and provide them with great results in minimum time.
Now let’s take a look at the types of testing a QA team can perform to make sure your product is secure, scalable, reliable, and does what it’s supposed to.
Types of testing to perform
To improve the efficiency of QA activities, a QA team has to decide which types of testing are better to perform manually and automatically. Dividing testing activities between manual and automated tests allows testers to minimize the time and effort required for each task.
Manual checks
Below is a list of testing types that the RubyGarage QA team performs manually:
- Usability testing. This type of testing is needed to check how easy it is to use your product. QA engineers perform actions a user can take and detect all bottlenecks that prevent a smooth user flow.
- Compatibility testing. Before testing starts, a client and QA team make a list of all devices, platforms, and browsers potential customers may use. A compatibility check is performed to make sure a product performs well in all these environments.
- Localization testing. If your product is supposed to work in different countries, localization testing is necessary to make sure the right content is displayed based on users’ locations.
- Performance testing. Traffic can be unpredictable. Performance testing checks how your product handles high data loads and user spikes.
- Security testing. Security testing allows a QA team to detect all vulnerabilities of your product that hackers can exploit.
Automated checks
When automating the following types of testing, a QA team can dramatically increase testing accuracy, reduce the testing time, shorten the time to market, increase test coverage, and more. Here are the tests the RubyGarage QA team performs automatically:
- Smoke testing. This type of testing allows a QA team to quickly ensure that a new build is stable and that the team can move on with testing.
- Functional testing. Full functional testing is aimed at checking every feature of a product to ensure it operates according to the specifications.
- Regression testing. Regression testing allows testers to assure that new functionality doesn’t have a negative impact on the existing codebase and doesn’t cause new bugs.
- Acceptance testing. This type of software testing is performed at the final stage of development, right before the product launch. It aims at assuring that the product meets critical business requirements and determining whether it can be released.
Wrapping up
The workflow we described in this post is based on best practices and aims at detecting all bugs at the early stages of a product lifecycle, speeding up the testing process and maximizing a QA team’s efficiency.
FAQ
-
Here are the steps a QA team takes to test your software product:
- Analyze requirements
- Plan tests
- Design test cases or checklists
- Run test cases or complete checklists
- Retest fixed bugs and perform regression testing
- Report on testing results
-
- Usability testing
- Compatibility testing
- Localization testing
- Performance testing
- Security testing
Find out how the RubyGarage QA team ensures flawless software products with the help of manual testing.
-
- Smoke testing
- Functional testing
- Regression testing
- Acceptance testing
Check out what automated testing services the RubyGarage team offers and how they can speed up your testing processes without compromising testing effectiveness