-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
Pros and Cons of Mobile Websites and Mobile Apps
In 2017, about 64% of the Earth's population owns a mobile phone, and according to Statista, this percentage keeps increasing. Statista suggests that by 2020 the number of mobile phone users worldwide will reach 5.07 billion. That's a pretty broad audience, isn’t it?

As a business owner or CEO, you certainly have thought about how to win this audience and what mobile strategy to apply: whether to build a mobile website or application. There's no single answer, as the option you choose depends on a number of factors including your business plans, your resources, and the web properties you might need.
At RubyGarage, we've built a number of projects based either on mobile website or a native app (or both). To help you in choosing the best solution for your business, we'd like to share our experience in this matter and bring out the benefits of mobile website and app as well as limitations of each approach.
Mobile Website
As with any other website, a mobile website is a browser-based way of accessing internet content. Unlike regular websites, it's designed specifically for mobile devices, and therefore is not displayed perfectly on desktop.
Along with mobile, there's another broader concept of optimizing websites for smaller screens: we're talking about a website with responsive design.
A responsive website contains HTML pages linked together, which are viewed in browsers over the internet. Here you won't find anything out of the ordinary. However, unlike regular websites, this particular type is geared to displaying correctly on all sizes of screens.
It works well not only with mobile-friendly websites and desktop versions of them, but also properly scales down for smartphones and tablets with touchscreen interfaces. Therefore a responsive web design goes perfect with mobile device just as much as a mobile website.

Responsive, or mobile websites work perfectly for implementing outreach strategies and supporting marketing or PR campaigns. As a mobile website is superior to a mobile application in matters of compatibility, accessibility, and maintenance, it is a great first step to boost and support your mobile marketing campaign.
To evaluate your choice between a mobile website and a mobile app precisely, though, let's touch upon the benefits of mobile website as well as its limitations.
Pros
- Compatibility. A website enhances the user experience across different types of mobile devices. In contrast, a mobile application requires developing a separate version for each operating system and device type. Users who own devices of different types may especially appreciate the benefits of compatibility that responsive websites provide. Besides, they support easy integration with other mobile features like QR codes and text messaging.
- Broader Reach. Due to the multi-device support that responsive web design provides across various platforms, it's becoming easy to reach a broader audience than a mobile app can reach. In the "app vs website" debate, the website definitely wins in terms of potential audience.
- Support and Maintenance. Websites also cost less to upgrade. You need to maintain just a single version of a them. Compared to mobile apps, which require downloading of every single update, responsive/mobile websites let you change the content or design just by editing them once, and allow you to do that efficiently and flexibly. After implementing, updates become active and visible immediately across all types of devices.
Cons
Mobile websites have a wider reach, better compatibility, and require less money than mobile applications. Still, they have their limitations.
-
Convenience. Unlike an application, a responsive/mobile website can't leverage all smartphone features as efficiently. Cameras, GPS, phone dialing, and other features integrated into mobile devices aren't always well developed for responsive/mobile websites, even though APIs and libraries aimed to help solve these issues have been appearing lately.
Another limitation to user benefits is a device's screen size. Of course, portability is the key reason why users enjoy having smaller devices on the go. However, mobile devices display a lot less content compared to a computer monitor or laptop screen. Both responsive design and mobile website don't fully access to all the content available on the desktop. Even though responsive web design adjusts to the screen size dynamically, still it doesn't make it completely convenient for users to surf the content on a mobile device. The same thing is with mobile website which actually reduces and rearranges the content available on the desktop.
- User Experience. Since mobile experiences significantly differ from desktop experiences, implementing the same interface for both platforms may harm your UX strategy. This mostly relates to the single-window restriction. The single-window restriction says that a user shouldn't have to leave their current page to access all the content they're looking for; however, with mobile sites it's often impossible to fit everything onto one page.
- Offline Access. Even if you design your mobile website in the lightest and most informative way possible, it still may work offline with only limited functionality using cached pages. Unlike a mobile application, which can run locally, a mobile website requires a good internet connection to operate fully.

Mobile App
Unlike responsive/mobile websites, which you can reach via browsers, mobile applications must be downloaded from specific portals such as the Google Play Market, App Store, or other market depending on the type of operation system.
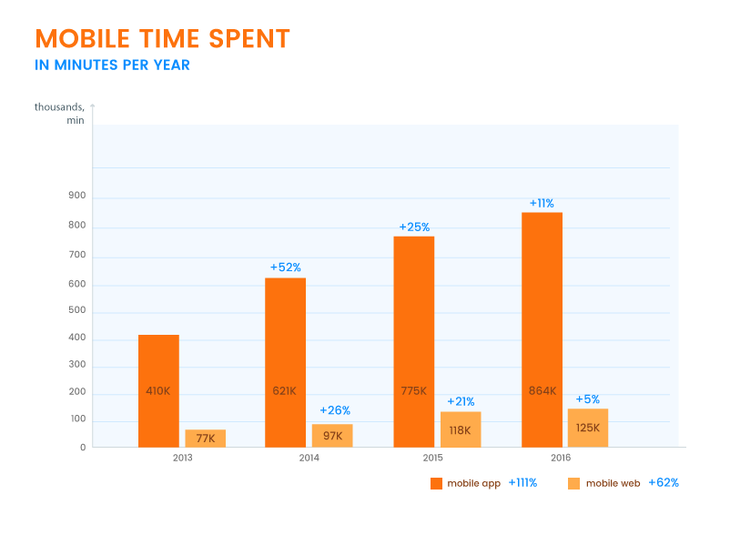
Mobile apps offer faster access to content and smoother interactions. Several recent statistics support the convenience of using mobile apps. According to Flurry Analytics' 2016 survey measuring time that mobile users are spending surfing the internet, 90% of users prefer using applications to mobile websites.

Another line of research by comScore affirms that from 2013 to 2016, the amount of time that mobile users spend surfing the web has grown more than 50%. Significantly, 90% of this growth relates to mobile applications.
Despite the pros of responsive web design, mobile apps seem to be way more popular. Before going through the pros and cons of mobile apps, however, let's first figure out when it makes sense to build a mobile app.
The Best Cases to Build a Mobile App
When it comes to specific business needs, there are common scenarios when building an application is the best solution. For instance, if you plan on setting up features linked to native device functionality, like GPS, click-to-call, cameras, or scanners, then an application will be more effective than a mobile website.
Another good time to choose an application is when you're building a platform such as a content marketplace or a social network that requires access to various types of content (images, texts, music, and Youtube videos) and needs to keep all these elements functional and dynamic.

An application is also perfect for interactive games (Angry Birds), tools for daily using (Evernote), and services that allow you to train and track real-time progress and that send regular reminders (FitBit, Duolingo).
Additionally, a mobile application is a reasonable solution for manipulating data. When you need to process complex calculations and build reports, such as in investment and banking, then it's also better to use an app.
For banking operations and services, a mobile app may work as a great addition to a complete website. Banks (Bank of America, Raiffeisen) nail this idea by picking out the most popular desktop web features, which are vital to use on-the-go, and putting only those features into their applications, making them easy and convenient to use.
Of course, to decide whether you need to build an application, it's important to investigate the key advantages of mobile apps as well as their drawbacks.
Pros
- Convenience. Analysis shows that the applications are more popular than equivalent websites, as they're more convenient. Mobile apps provide better user experiences, load content faster, and are easier to use. Besides, unlike websites, apps have push notifications. Sharing updates, special features, and reminders within an app increases customer loyalty and retention. Also, the design of mobile apps fits different screen sizes more elegantly than websites.
- Personalization. Mobile apps are a great solution for services that require regular use. An application allows users to set preferences, create personal accounts, and keep vital information at hand. From a business point of view, mobile apps provide better support for targeting an audience and therefore building marketing campaigns for different groups of users.
- Working offline. Another crucial advantage related to mobile apps is the opportunity to use them offline. As apps are installed on a mobile device, they can keep providing access to content and features even without an internet connection.
Cons
-
Compatibility. To ensure proper functioning, a mobile application should meet the requirements of the particular operating system. This means that every platform – iOS, Android, and Windows – requires a separate app version.
Of course, it's possible to develop a cross-platform solution that's supposed to fit every operating system and device.
However, cross-platform application frameworks don't provide full support for every module and feature of each operating system. For instance, a cross-platform framework may not support 3D graphics, which in turn may lead to limitations in creating and displaying app designs. Restrictions like these may have an impact on the stability of app features, and may lead to sub-optimal functionality.
- Support and Maintenance. When an application is developed for several different platforms, supporting it also takes more time and money. Indeed, you need to provide upgrades and fix compatibility issues for every type of device – and do so regularly. Besides, you have to inform your users about these updates and push them to download the updated version of the app. Another issue related to maintaining an application is the time and effort needed to get approval from the markets where the app is placed.

Comparison Summary
The "mobile app vs mobile website" issue will remain topical for business owners. While considering if it's better to choose a mobile website or an app for your project, you may refer to the following table where we have summarized the benefits and limitations of both approaches.
| Criteria | Responsive/Mobile Website | Mobile App |
Compatibility |
Displays equally well on all types of devices |
Requires development of separate version for each platform |
Reach |
Reaches wider audience; covers all devices (mobile, desktop, laptop) |
Accessible for smartphone and tablet users only |
Working Offline |
Limited offline functionality |
Works well offline |
Ongoing Maintenance |
Supporting and updating across all mobile devices is easier; flexible; requires less effort |
Requires extra time and cost for regular updating, including time for approval from app markets |
Convenience |
Provides limited convenience due to screen size and inability to keep all needed info on one page |
Provides better experience in regular use; loads content faster; has push notifications |
Personalization |
Provides average opportunities to personalize settings |
Provides wider options for personalization |
Every company in every business sphere must make its own choice depending on its business strategy, marketing goals, and brand positioning. The choice is not about picking one of the two, but rather about finding the right solution that will provide the best results for your business. Besides, a mobile strategy can reasonably include both a mobile website and an app.