-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
How Telemedicine Is Transforming Healthcare: Key Points and Trends
Over a decade ago, telemedicine became a game-changer in the healthcare industry. Although virtual medical care was technologically feasible, service providers, physicians, payers, and patients adopted it quite slowly. The situation drastically changed with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic. The demand for telehealth services started growing exponentially, and telemedicine is expected to remain prominent even after the pandemic is over.
If you want to not only know how telemedicine is transforming healthcare but also influence the future of millions of patients by developing helpful remote patient monitoring platforms, doctor appointment apps, or other telehealth software, this guide is for you!
What is telemedicine?
Telemedicine is the delivery of healthcare services, where distance is a critical factor, by all healthcare professionals using information and communication technologies for the exchange of valid information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation, and for the continuing education of healthcare providers, all in the interests of advancing the health of individuals and their communities.
Telemedicine began several decades ago with providing consultations and care to patients in remote and rural regions. It is now well integrated into the day-to-day operations of private clinics, state hospitals, and patients’ homes.
Telemedicine goals
To understand how telemedicine is transforming healthcare, let’s first look at what it hopes to achieve:
- Provide patients from rural or remote regions with increased access to healthcare services.
- Improve communication between patients and physicians.
- Allow patients to select from a wide range of doctors regardless of their location.
- Make virtual visits more convenient for patients who have limited time or experience transportation difficulties.
- Provide people with limited mobility with increased access to healthcare services.
Scope of existing telemedicine services
Thanks to recent policy changes initiated by the American Medical Association that removed or minimized several barriers to the adoption of telemedicine services, telehealth has become more accessible. Now patients can access many virtual healthcare services that improve patient outcomes and make patient–physician communication more efficient. Services include:
- Remote appointment scheduling
- Patient screenings
- Receiving and forwarding test results to medical specialists
- Following up with patients after hospital discharge
- Remote monitoring of clinical signs of chronic conditions
- Answering urgent questions
- Managing prescriptions
- Nutrition consulting
- Coaching and consultations for people with chronic diseases
- Caregiver support
- Support and care for patients living in long-term healthcare facilities
- Training for healthcare providers located in remote regions
According to the 2020 Amwell Physician and Consumer Survey, the rapidly increasing demand for virtual specialty care has encouraged specialists from different medical fields to offer telemedicine services. These findings demonstrate the year-over-year growth in the adoption of telehealth among doctors and their general understanding of how technology has changed medicine.
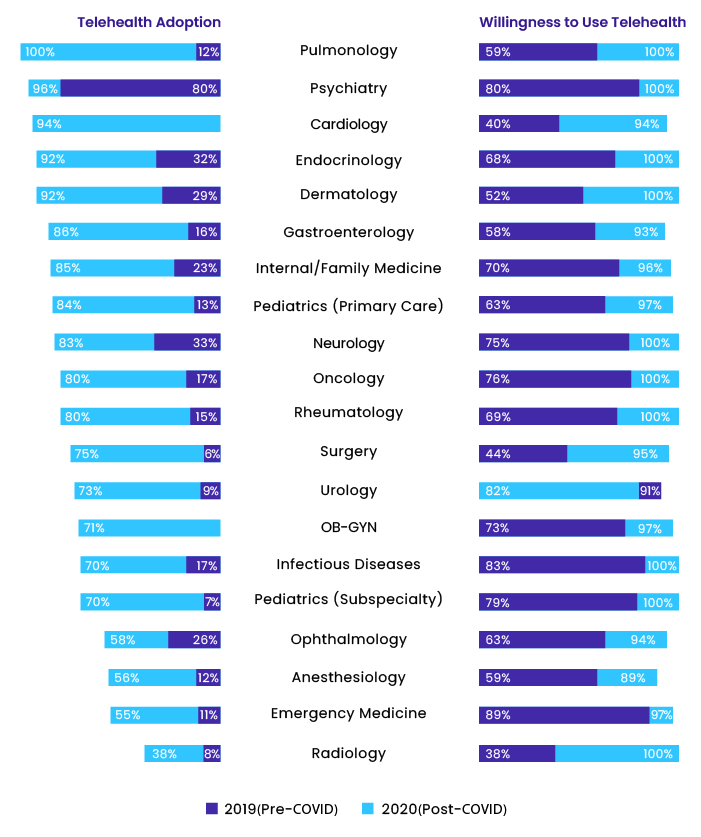
Image source
Types of telehealth services
To use telemedicine wisely, you need to understand the three main types of telehealth.
- Synchronous telehealth, also regarded as “virtual visits,” is live patient–physician communication via phone, chat, or video call in order to evaluate a patient's state and get the information needed for a diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Asynchronous telehealth, also called “store-and-forward,” is a platform patients and doctors use to transmit test results or medical records to medical experts who analyze them, give consultations, make diagnoses, and prescribe medication. This type of software can also be used to answer questions, make appointments, discuss symptoms, store a patient’s health history, etc. Patients may utilize asynchronous telehealth by uploading images that demonstrate their symptoms or physical condition, answering questions on online forms, and using applications or devices to control their vitals.
- Remote monitoring, or “telemonitoring,” allows consumers of telemedicine services to use medical devices at home to get reliable data sent directly to their physicians, who are able to monitor their condition and change treatment if needed. This type of telemedicine service can be used to take care of patients with chronic illnesses or those discharged from the hospital.
How telemedicine is transforming healthcare
This list of telemedicine advantages and disadvantages will give you a clear idea of how telehealth technology has changed medicine.
Key advantages of telemedicine
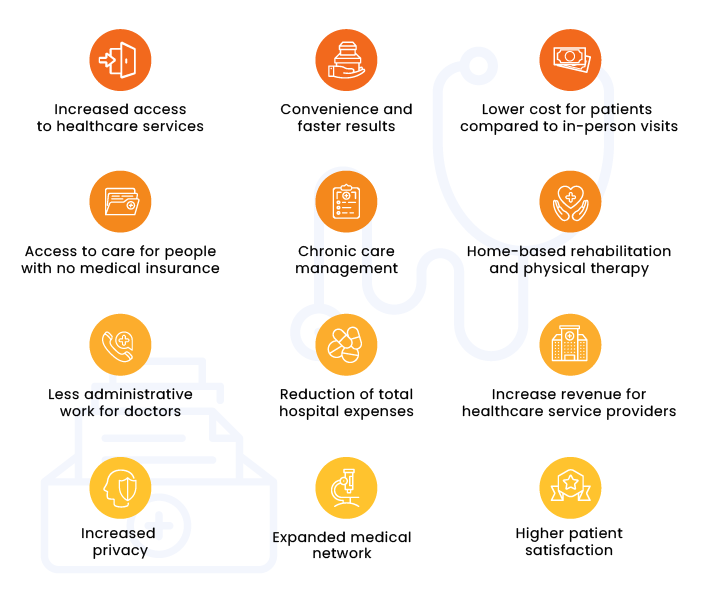
Increased access to healthcare services
Through telehealth, patients have access to urgent medical care when they are unable to visit a doctor in person because of after-hours needs, absence of local specialists, urgent problems, etc. Telehealth appointments are a solution for people living in rural areas. On average, the nearest hospital for a person living in a rural area is located 10.6 miles away from home, while for a person in an urban area, a hospital is located on average only 4.4 miles away. A virtual support from a doctor can be vital in a time-sensitive situation.
Convenience and faster results
Patients can arrange virtual appointments on a convenient day and time. The wait time is shorter, and patients can get medical results and treatment recommendations more quickly. Virtual visits help decrease patient stress and improve their experience.
Lower cost for patients compared to in-person visits
For patients, virtual consultations are cheaper than in-person visits. Additionally, many insurance companies have added virtual services coverage to their plans.
Access to care for people with no medical insurance
While in-person visits to hospitals can be cost prohibitive for patients who don’t have health insurance, virtual appointments with medical specialists are an alternative.
Chronic care management
In the US, approximately 100 million people with chronic diseases account for 75 percent of healthcare expenditures. Thanks to regular online consultations and support, doctors can control a patient’s condition and easily make treatment changes. The use of telemedicine services also helps reduce the number of hospitalizations, cut costs, and improve patients’ health.
Increased privacy
Patients don’t need to go to hospitals in person when using telemedicine services, allowing their interactions with doctors to stay private.
Expanded medical network
With telemedicine, patients can receive treatment from a medical professional living in any part of the world. Additionally, doctors can discuss a patient’s state with colleagues and jointly decide on the best treatment.
Home-based rehabilitation and physical therapy
Physical therapists can supervise at-home exercises. Doctors can also provide virtual guidance and support to patients who need rehabilitation after surgery.
Higher patient satisfaction
Patients who utilize telemedicine services are more satisfied with the quality of care. According to the COVID-19 Telehealth Impact Study, over 75% of patients who used telemedicine services in 2020 were fully satisfied, and 70% of survey participants said they would use virtual healthcare services in the near future.
Less administrative work for doctors
Since telemedicine services are digitized, many routine operations done by healthcare professionals are automated, enabling doctors to focus on patient examination and consultation instead of administrative work.
Reduction of total hospital expenses
Online visits do not require an office space or additional staff. If hospitals can move patients who don’t need hospital treatment to remote care, it will optimize office workloads and cut overall medical costs.
Increased revenue for healthcare service providers
Telemedicine helps doctors consult with more patients within the same time frame. Thus, providers can increase revenue without adding more physicians.
Key disadvantages of telemedicine
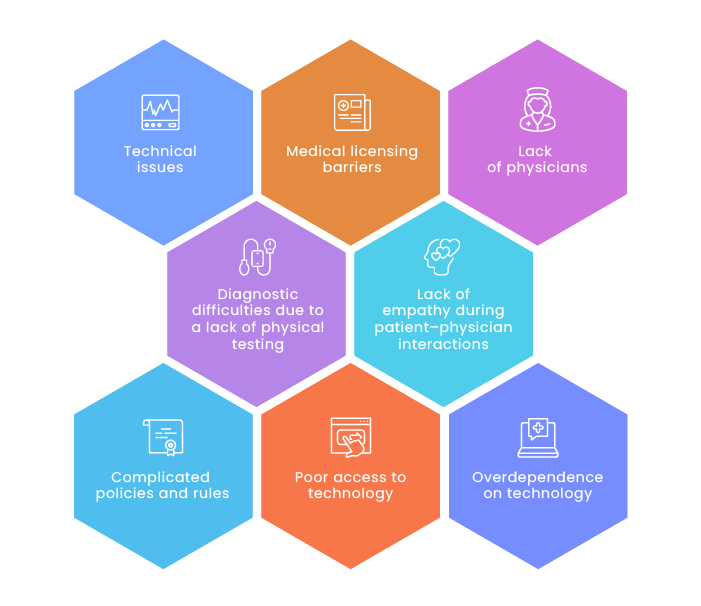
Diagnostic difficulties due to a lack of physical testing
The inability to conduct medical testing in person has the potential to lead to increased consultation times, as physicians may need to ask additional questions to understand the problem and make a diagnosis.
Lack of empathy during patient–physician interactions
Electronic devices remove the human touch from treatment and may result in confusion and frustration, especially among older patients who may be unfamiliar with telemedicine technology and how it has changed medicine.
Poor access to technology
Telemedicine requires access to the internet and communication devices. However, at-risk or vulnerable populations may be unaware of telemedicine options or may lack devices needed for virtual consultations.
Technical issues
Since telemedicine services utilize advanced technologies, patients and service providers need to know how to solve connectivity or other technical issues that may occur during virtual consultations.
Lack of physicians
According to The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections from 2019-2034 report by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), US healthcare is expected to suffer severe shortages in physicians in the near future (121,300 doctors by 2030). This is particularly concerning as the population is estimated to grow by 10.6 percent (from 328 million to 363 million), and the number of people aged 65 and older is estimated to grow by 42.4 percent by 2034. Finding available appointments and medical experts has become and will continue to be a challenge for patients.
Medical licensing barriers
US states generally require clinicians to have a license in the patient’s state for telemedicine services provision, and it may be challenging for doctors to acquire multiple licenses (granted by separate states) in order to consult patients from around the country.
Overdependence on technology
A unified information system connects hospital departments. If one department is down, doctors from other departments won’t be able to access information, delaying medical procedures. This is an inconvenience which may also have adverse effects on a person’s health.
Complicated policies and rules
The telemedicine industry has experienced rapid growth, so current healthcare policies and rules may lead to difficulties in service implementation.
Telemedicine prospects and trends
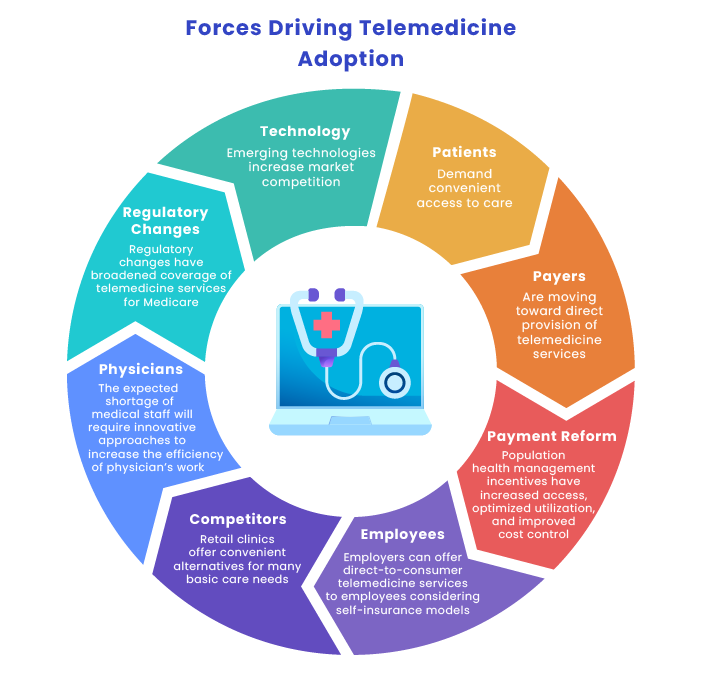
While traditional healthcare providers continue responding to COVID-related challenges and attempt to return to business as usual, virtual care suppliers have an opportunity to create a new standard of care.
To better understand how telemedicine is transforming healthcare and how to boost telehealth adoption, we first need to determine what influences the adoption of telemedicine.
The following trends in telemedicine are expected in the near future:
Active use of AI for the development of telemedicine devices
Psychiatric care teams will use AI-embedded high-definition video conference calls to analyze patients' facial cues to determine their current emotional state. Other specialists will also use AI to improve patient care.
Self-service telemedicine kiosks in schools, offices, and other institutions
Active distribution of self-service kiosks will help people monitor their health and provide them with immediate help.
Reorganization of medical care financing and legislation
Though current financing is predominantly focused on traditional hospital facilities, soon there will be a shift to more investment in telemedicine, as it appears to be more efficient and less expensive. Current laws and regulations will also be changed to accommodate telemedicine.
Acceleration of innovation in telemedicine
Further expansion of telemedicine services adoption and a clear understanding of how telemedicine is transforming healthcare will require improvements in existing devices and the development of new technologies that will meet patient and provider needs.
Transformation of health care due to 5G
5G will help provide fast data transfers. It will also make communication between medical specialists and patients smoother and more efficient, and surgeons who use AI to perform operations will no longer need to worry about issues related to internet connectivity delays.
New spaces for health facilities functioning as remote care centers
Due to the increased use of technology, hospitals, nursing homes, and doctors’ offices will adapt to include equipment (cameras, speakers, secure connections, and monitors) in order to function as remote care centers.
Telemedicine challenges to combat
The COVID-19 pandemic helped break down many barriers that slowed the implementation of virtual health apps into the healthcare system. However, there are still challenges telehealth service providers need to address.
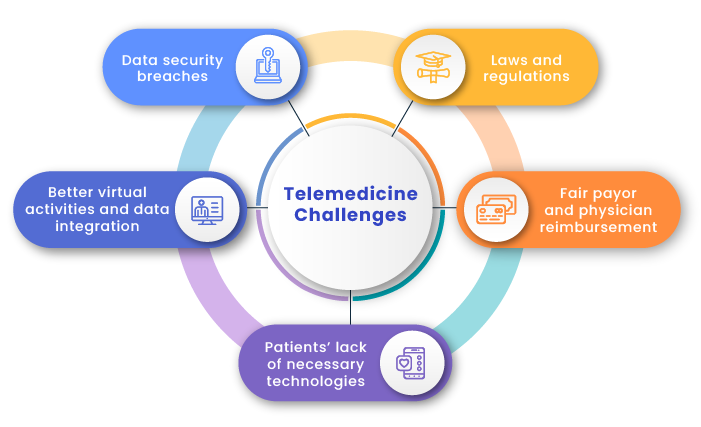
Data security breaches
Telemedicine implies the electronic transfer of patient health records to doctors, so it’s critical to ensure a secure connection, protect personal data, and guard against potential breaches and threats.
Laws and regulations
Virtual care solutions must comply with HIPAA rules. Providers also need to obtain licenses and certifications to operate in individual states.
Better virtual activities and data integration
The growth of the telemedicine ecosystem requires better data integration across devices and users. Telehealth service providers also need to understand how to better integrate virtual health-related activities into doctors’ daily operations to create hybrid care models that comprise in-person and virtual services.
Fair payor and physician reimbursement
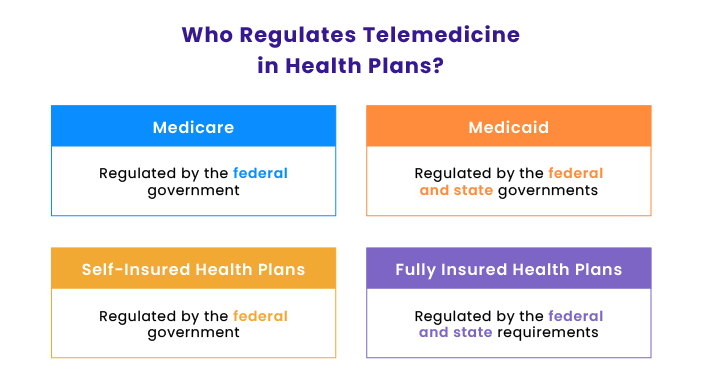
With a myriad of healthcare laws and regulations in place, it’s challenging both for patients to understand who can offer virtual medical services and for service providers to understand how they will be reimbursed. Fully-insured plan and Medicaid telehealth coverage is regulated predominantly by individual states, while the federal government controls reimbursement and coverage of telehealth services for Medicare.
Service providers need to develop a transparent reimbursement system for doctors, as this aspect is currently not adequately regulated.
Patients’ lack of necessary technologies
Telemedicine providers need to develop reliable infrastructure for providing healthcare services while ensuring patients will be able to support the developed technologies on their end. Often, people belonging to vulnerable segments of the population don’t have a phone to accept a call or an internet connection to make a virtual appointment.
Types of telehealth solutions that will be in demand
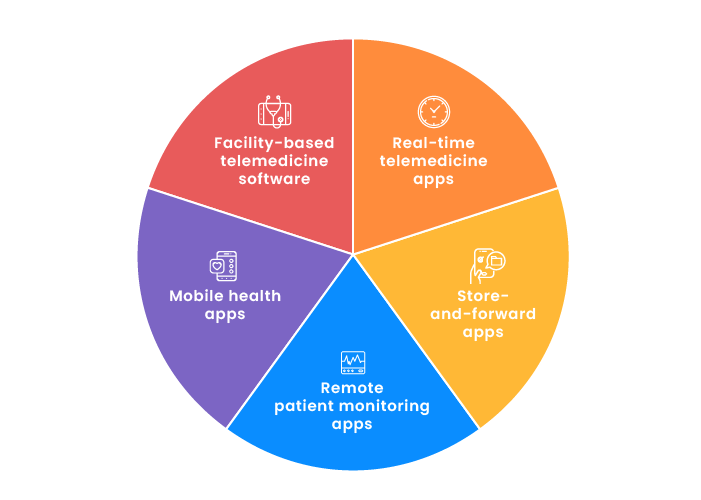
Real-time telemedicine apps provide patient–physician or physician–physician interaction in real time via phone, video conference calls, chats, etc.
Store-and-forward apps gather and analyze patient data and forward it to health professionals who diagnose and prescribe medication.
Remote patient monitoring apps monitor a patient’s health state at home with the help of medical devices like glucose meters, heart rate monitors, etc. All data is sent to a health platform where medical specialists observe a patient’s condition in order to prevent severe problems.
Mobile health apps monitor chronic diseases, provide access to patient data and make healthcare services more accessible and efficient.
Facility-based telemedicine software aims to connect healthcare service providers across different departments and partner facilities.
Final thoughts
Telemedicine use has increased rapidly, and it will continue to grow after the end of the COVID-19 pandemic. Though healthcare providers face many challenges, they also have a wide range of opportunities for growth and market expansion.
FAQ
-
Telemedicine is the delivery of healthcare services by all healthcare professionals using information and communication technologies for the exchange of valid information for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and injuries, research and evaluation, and for the continuing education of healthcare providers.
-
There are three main types of telehealth: synchronous telehealth, asynchronous telehealth, and remote monitoring.
-
The following trends in telemedicine are expected in the near future:
- Active use of AI for the development of telemedicine devices
- Self-service telemedicine kiosks in schools, offices, and other institutions
- Reorganization of medical care financing and legislation
- Acceleration of innovation in telemedicine
- Transformation of health care due to 5G
- New spaces for health facilities functioning as remote care centers










