-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
Top UX Research Methods to Build a Successful Product
Designing successful software is impossible without thorough preliminary user experience (UX) research. Without it, how can you make sure your product is convenient and elicits only positive emotions? In this article, we look at popular UX research methods to figure out their purpose, which fits your project, and more.
Why UX research is important
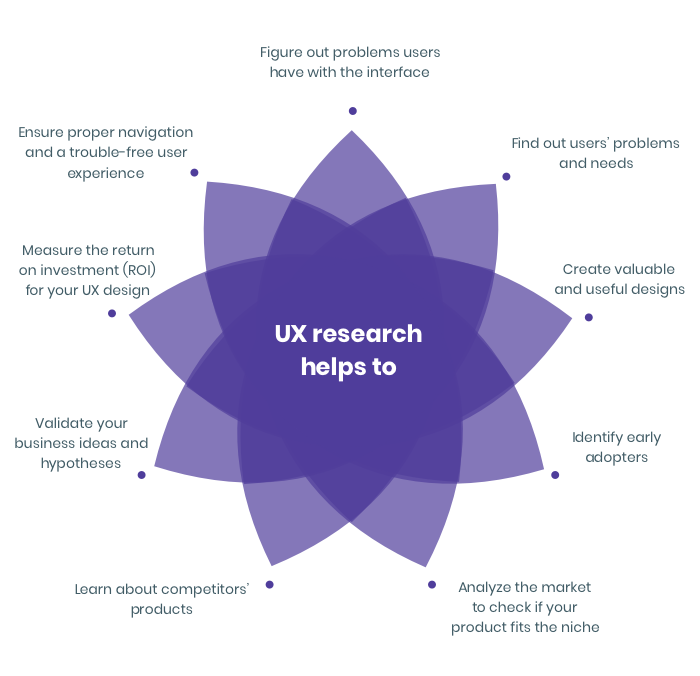
Many business owners don’t understand the importance of conducting UX research at the very beginning of product design. Probably, they’re just unaware of how in-depth UX research can impact product performance and the overall user experience. So why does UX research matter? In short, it helps you:
- figure out problems users have with the interface
- find out users’ problems and needs
- create valuable and useful designs
- ensure proper navigation and a trouble-free user experience
- measure the return on investment (ROI) for your UX design
- identify early adopters
- validate your business ideas and hypotheses
- learn about competitors’ products
- analyze the market to check if your product fits the niche
The most common camps of UX research methodologies
Primary and secondary research
Primary user research method is original research of the design team. It’s usually conducted to find out who you’re creating the product for and why. This type of UX research allows stakeholders to validate the business idea and provides meaningful design solutions. Usually, this data is gathered by means of surveys, questionnaires, and interviews with users.
Secondary research is executed by analyzing and interpreting data from the internet, books, and any studies on your topic. This type of UX research is used by a design team to support the ideas and insights obtained from the primary research.
| Primary research | Secondary research | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Low |
| Time | Long | Short |
| Carried out by | UX researcher | Third party |
| Data | Specific to the needs of the UX researcher | May not be specific to the needs of the researcher |
Generative and evaluative research
Generative user research method is usually conducted at the beginning of the research process. It focuses on defining the problem the business is trying to solve and the best possible ways to solve it. To define the problem and solutions, you should first understand your potential customers’ or users’ lives, behaviors, attitudes, preferences, and perceptions. Generative research allows you to get rich data on your target audience so you can craft the most beneficial design solutions based on these insights. This research is valuable since it shows you whether your product fits the market and solves a particular problem.
Evaluative user research method is executed throughout the whole development lifecycle, from concept design to final product. This method is used to test the existing product to see if it meets your users’ needs and delivers a seamless user experience.
| Generative research | Evaluative research | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To define a problem and come up with a solution | To assess the effectiveness of an existing product |
| Orientation | Future | Present and near future |
| Time | Start of the research process | Throughout product development |
Qualitative and quantitative research
Quantitative research provides a UX researcher with numerical values that answer questions like how much, how often, and how many. Data gathered from quantitative research answers concrete questions.
Qualitative user research method (or empirical research) produces insights in the form of people’s feelings, observations, and preferences. This type of research is valuable because it gives you rich data on how users think. Knowing what’s in your users’ minds gives you an opportunity to create a successful project.
| Quantitative research | Qualitative research | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To test hypotheses | To discover ideas |
| Approach | Measure and test | Observe and interpret |
| Data format | Number-based | Text-based |
| Researcher | Uninvolved | Involved |
| Method | Surveys, interviews, observations | Review of documents |
The most popular UX research methods from all methodologies
User interviews
During user interviews, a designer or UX researcher asks users questions about the topic of interest. The purpose of the questions depends on what the researcher is trying to learn. Interviews provide insights into what users like, how they feel when using a product, what you can improve, and so on. User interviews can be done:
- Before the design process to create user personas and user journey maps
- At the end of usability testing to observe user behavior and collect responses
User surveys
User surveys can help businesses get data about users or potential users. At the same time, conducting a user survey can be risky if you ask the wrong questions. A user survey usually includes a set of questions aimed at understanding users’ preferences and attitudes about a product. These surveys are given to a sample audience that represents a larger target group.
Mainly, the questions in user surveys fall into two categories: open and closed. Open questions allow users to answer as they wish. Researchers use these questions to get qualitative information about user behavior. Closed questions give quantitative information and include a set of possible responses (yes/no, numerical scale, multiple choice, etc.)

Usability testing
Usability testing shows how real users use a product. In usability testing, users are asked to conduct a task while a UX researcher observes whether they encounter any obstacles. If the researcher sees that several people experience the same confusion while completing this task, they’ll provide a list of recommendations to overcome the issue.
Card sorting
Card sorting is a useful UX research technique, since it provides insights into how data is structured in the user’s mind. After this type of research, a design team can better understand how to structure an app or website. Card sorting falls into two categories: open and closed. In open card sorting, people are asked to sort a deck of cards into groups they invent and to explain their reasoning.

In closed card sorting, people are asked to sort cards into groups established by researchers.

This technique is a simple, fast, and cheap way for businesses to understand how their users think.
Benchmarking analysis
Benchmarking analysis reviews how the existing design affects the user experience. In general, there are two ways to benchmark:
- Standalone benchmarking: Usability benchmarking is usually used to redesign a project. It establishes the starting point which can help to find out if your design iterations impact the overall UX.
- Competitive analysis: This analysis allows to interpret the website usability in reference to the competitors.
Summing up
Depending on the project you’re working on, your design team can choose several methods to get a solid base for further product design and development.
For example, the RubyGarage design studio take a research-driven approach, which means we pay close attention to the research phase. We prefer to use benchmarking analysis and usability testing to choose the right start for the project and review our solutions during the whole design process.