-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
PCI DSS Non-compliance: Fees and Other Consequences You Need to Know About
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) was established by Visa, Mastercard, and other credit card giants back in the early 2000s to protect cardholders’ information. As an international standard, it requires any company that somehow deals with clients’ credit card information to stick to its requirements. If they fail to do this, companies are held accountable and face penalties.
In our article, we have a close look at fees and other common consequences of PCI non-compliance.
#1 Fees and penalties for non-compliance
The size of the non-compliance fee that the PCI DSS Council imposes on a company depends on two factors.
The first is the company’s size, which is determined by the number of transactions it processes per year. Based on this factor, all companies are divided into four levels. Fourth-level companies usually don’t face fines, while first-level companies face the greatest financial responsibility for non-compliance.
The second factor that influences the sum of a fine is the period of non-compliance with the standard. Companies that haven’t been compliant for a month pay less than those that have been non-compliant for seven months, for instance. Fines are imposed monthly until a company meets the standard.
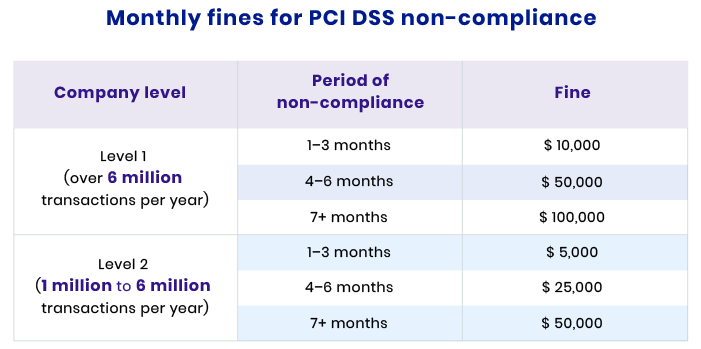
In the image below, you can see how the size of a fine varies for first- and second-level companies:
#2 Revoked right to process transactions
An acquiring bank is a bank that processes your company’s transactions, and it’s that bank’s duty to keep track of your PCI DSS compliance. If a bank discovers that your company isn’t compliant, they must inform the council about it. Once this information is disclosed, the council will insist on you becoming compliant. However, this is a long and costly process, so you might not be forced to do it immediately.
However, if you don’t move towards becoming PCI DSS compliant, you can eventually be denied the right to process transactions. This rejection might originate from either the council or your acquiring bank.
#3 Fees and penalties for data loss
If hackers manage to steal your customers’ data, you’re responsible for the leakage even if you’re PCI compliant. In this case, you’ll need to compensate up to $90 per compromised credit card record. Moreover, a security breach leads to a fine of up to half a million dollars depending on the severity of the case. However, the total amount of the fine can exceed even your worst expectations.
Target, one of the biggest retail corporations in the USA, experienced a hacker attack in 2013. During three weeks of manipulations by a hacker, Target lost credit card data of 40 million customers. As a result, the company spent almost $150 million to settle the issue. What’s most shocking about this situation is that Target had installed new malware detectors in their security system six months before the attack.
Another example is Equifax, an American credit reporting agency, which is held accountable for losing the personal data of 147 million people back in 2017. To settle the consequences of the data breach, Equifax agreed to pay more than $550 million.
There are many more examples of large corporations that, despite their advanced security systems, became victims of hackers.
#4 Costs of potential lawsuits
Another consequence your company might experience is lawsuits, and there are several ways you can face them:
- Data breach. If your actions somehow lead to a data breach, your customers might want to take legal actions against your company for letting this happen. The recent case with UK EasyJet airlines shows that such situations can be really hard for companies to handle, especially if one company must defend itself against a class-action lawsuit supported by more than nine million customers.
- PCI DSS non-compliance can frequently become a reason for credit card associations to sue your company. Or an acquiring bank can be a complainant in court if they decide your company is accountable for any issues connected with the insecurity of cardholders’ data. This was the case when two American banks sued Target and Trustwave Holdings, Inc to compensate $5 million for the consequences of the 2014 Target data breach.
- Lawsuits filed by you. Another scenario is if your company files a lawsuit against an acquiring bank or credit card association claiming their penalties aren’t fair. A similar lawsuit was initiated by Genesco against Visa and Mastercard. Genesco, a large American branded footwear retailer, sued the credit card companies for imposing a fine for data leakage without real evidence. However, even if the law is on your side, it will take a lot of time and effort to prove your point.
#5 Lost reputation
Although cases of PCI non-compliance aren’t revealed to the public unless they’re really serious, your company’s reputation still might suffer. Acquiring banks and credit card companies will hardly bother to ruin your reputation. But sooner or later, your customers can find out that your company isn’t reliable in terms of data security. Once that happens, they’ll think twice before paying for your products or services. Moreover, they’ll hardly recommend you to their friends and family. Thus, you can lose your existing customers as well as potential ones.
If your company is caught for being PCI non-compliant or people start discussing any issues related to possible data breaches for which you are at fault, here are some tips to save your reputation:
- Look for customer-focused solutions. Be customer-oriented whatever it takes. Think of how you can stop the data breach or compensate your customers for lost information. Also, consider ways to better protect your customers’ information in the future.
- Make fast yet thoughtful decisions. Being guilty of losing your customer’s data isn’t enjoyable and can put pressure on your company’s management. Still, you should try to improve the situation as fast as possible.
- Become PCI DSS compliant. This standard is the only one of its kind that guarantees your company is safe to cooperate with when it comes to processing information. Becoming PCI DSS compliant can minimize the possibility of hacker attacks and data loss in the future.
#6 Increasing customer churn
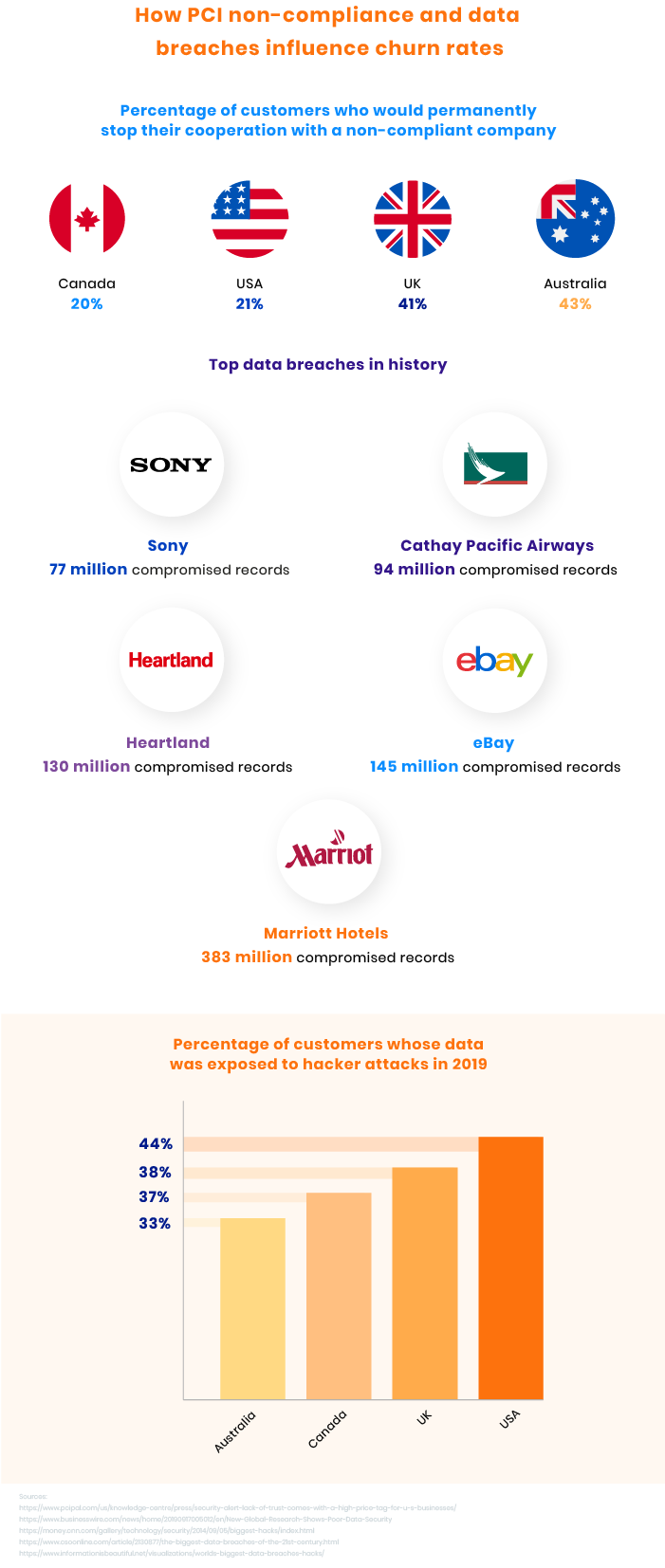
Surveys by BusinessWire reveal that up to 85 percent of consumers would stop their cooperation with a company after a major data breach. Can you imagine losing 85 percent of your customers? How much money and effort would you have to spend to return at least part of those dissatisfied consumers?
In the infographics below, you can see possible rates of customer churn for a PCI non-compliant company as well as other negative consequences your company can experience.
#7 Decreased revenue
This consequence is closely related to increased customer churn. Once you lose customers, you lose profits. You’ll also need to spend money on PCI non-compliance fees, compensation, and other issues to recover from your failure to meet the standard.
How to avoid fees and other consequences of PCI non-compliance?
Obtaining and maintaining PCI DSS compliance can cost companies hundreds of thousands of dollars. However, non-compliance can turn out to be several or even a dozen times more expensive. So take care of meeting the standard to ensure the security of your customers’ data as well as your business.
FAQ
-
Non-compliance can result in different troubles for your business, the most common of which are:
- Monthly fines
- Revoked right to process transactions
- Penalties for data breaches
- Lawsuits
- Reputational losses
- Customer churn
- Decreased revenue
-
The size of a fine depends on the size of your business as well as the period of non-compliance. Fines vary from $5 to $100,000 per month. If you want to check your company for PCI compliance, contact us for a professional audit.
-
Examples of large corporations that have experienced legal proceedings connected with PCI DSS non-compliance demonstrate that there are two kinds of lawsuits:
- Lawsuits filed by a company’s customers
- Lawsuits filed by an acquiring bank or by credit card companies