-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
Music Industry Problems and How They Can Be Solved with the Blockchain
Today we see various industries, including creative ones, adopting new technologies to change for the better. And now some people claim that using the blockchain in the music industry can solve the industry’s main problems.
So how can blockchain technology help artists? To answer this question, let’s take a look at the industry’s common problems.
Lack of a single database
The music industry lacks a global registry of musical recordings that would contain information on their creators and owners. What we have today is a number of databases, but the information they provide may vary.
Blockchain technology can make it possible to create a single database of musical creators and their works. Moreover, this database could provide contact information for music owners as well as terms of use.
Middlesex University’s report titled Music on the Blockchain reveals how bringing music and the blockchain together can influence the industry. As the report states, the blockchain can be both a database and a network, allowing information to sit on a distributed ledger rather than in silos.
Need for an intermediary
Over the years, the music industry has worked in a way that has made musicians rely on labels, distributors, and promoters. But with this model, artists often face complicated revenue distribution systems where every intermediary takes part of the income. That’s why music distribution is still an issue for artists.
How can we deal with this problem?
Blockchain technology lets music creators publish their works and sell them directly to fans without a third party. As a result, it eliminates the need for publishers and distributors.

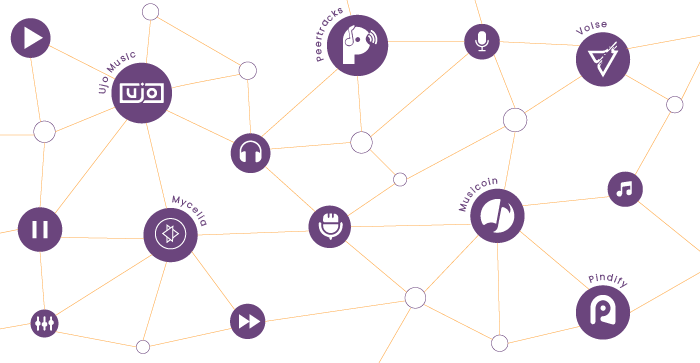
Let’s take Pindify, a blockchain-based platform that RubyGarage built, as an example. Pindify is a marketplace where musicians and other creatives can share their works and earn money. Moreover, Pindify is a network platform since it enables communication between artists and their fans. Pindify has even offered users to participate in an ICO.
Royalty issues
According to the International Federation of the Phonographic Industry’s Global Music Report, 2017 saw 41.1 percent growth in streaming revenue. But to upload music to Spotify, for instance, musicians need distributors. Taking into account the pretty complicated formula that Spotify uses to distribute royalties, this distributor often receives a significant part of the income. Moreover, the revenue that artists get may vary depending on their contract with their label. Over the years, even the biggest music streaming services have been occasionally accused of underpayment. Some popular musicians, including Taylor Swift and Adele, have decided to remove their albums from streaming services, citing unfair payment practices.
Let’s see how using the blockchain in the music industry can help solve this particular issue. Being a transparent system, the blockchain enables music creators to receive payments directly, bypassing intermediaries. With its help, musicians and their fans can make peer-to-peer exchanges securely, using smart contracts that guarantee transparency. Stored on the blockchain, these contracts can include a specific percentage of income that rights holders get directly. With a smart contract, revenue can be automatically divided, letting musicians receive payments immediately and directly from their listeners.
For instance, the founders of Ujo Music state that with their blockchain music platform, rights owners can design licenses themselves and receive automated royalty payments. Thus, musicians can have more control over their recordings and revenue.
We’re trying to create a system that’s fair for the artists first and foremost.
Copyright issues
To use someone else’s work of art, you need to get the rights holder’s permission. This sounds simple, but in reality this process often turns out to be more complicated and time-consuming than one would expect. Moreover, licensing and collecting performance royalties usually involves publishing companies and organizations like BMI and ASCAP that protect musical copyrights. It often takes some real effort to find out who you actually need to pay to use copyrighted music.
With blockchain technology, each musical recording can contain metadata with information regarding copyrights and terms of use. This would simplify the process of getting a license to use copyrighted music. Moreover, this technology would make tracking plays easier as well. It’s possible to protect music with the blockchain.
Several musical artists have already released singles or full albums on the blockchain. One of them is Imogen Heap. As Heap explains, she would like to avoid situations when other artists get their content taken down for using her music. One of the advantages of the blockchain for music artists is that it simplifies the process of collaboration by making it clearer and more transparent.
Blockchain has the potential to provide a more quick and seamless experience for anyone involved with creating or interacting with music.
Imogen Heap has also founded Mycelia, another blockchain music platform where artists can get paid fairly without having to involve distributors or other third parties, giving musicians more control over their works.
Monetizing the fan base
Building a fan base is vital for every artist since with its help the artist can make a living. Even when you already have a fan base, however, monetizing it can be quite a challenge when taking into account the terms that streaming services and publishing companies offer.
Using the blockchain for music sharing, artists can get solid support from their fans. The blockchain gives listeners the possibility to select a song or album and immediately pay for it. And it’s more convenient to make micropayments with cryptocurrencies due to small transaction fees.
To release Utopia, Björk teamed up with Blockpool, which lets people pay for this album with cryptocurrencies.
Another example is RAC’s EGO. To release his album on the Ethereum blockchain, RAC collaborated with Ujo. Jesse Grushack, founder of Ujo, notes that the artist managed to make even more money from tips than from sales. So it’s safe to say that fans are more likely to buy their favorite musicians’ records when they know exactly where their money will go.
If you want to know more about the blockchain and other technologies, follow our blog.