-
Product Management
Software Testing
Technology Consulting
-
Multi-Vendor Marketplace
Online StoreCreate an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solutionCustom MarketplaceGet a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to marketTelemedicine SoftwareGet a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirementsChat AppGet a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platformsCustom Booking SystemImprove your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solutionVideo ConferencingAdjust our video conferencing solution for your business needsFor EnterpriseScale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutionsFor StartupsTurn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions -
-
- Case Studies
- Blog
Best Ecommerce Testing Practices to Identify Issues That Drive Away Your Customers
One of the main functions of ecommerce websites is to make it comfortable for customers to buy a company’s products. If there are bugs or the purchasing process is too complicated, users will close your website and find another one. Ecommerce testing helps you check if the purchasing process on your website is streamlined enough to boost sales, decrease cart abandonment, and improve customer satisfaction.
In comparison with other types of software testing, ecommerce testing has its own peculiarities. In this article, we’ll review the main things you need to know about ecommerce website testing.
Top usability issues on modern ecommerce websites
Let’s review the most common problems with ecommerce projects that make users leave without placing orders.
#1 Issues with registration and checkout forms
No show password button
When creating a new account on a website, a user often needs to enter the password twice. The password is usually hidden and, if the password fields don’t match, the user will need to fill in both fields again. This takes time and can be annoying. You can fix it by adding a button to show the password so the users can make sure they’ve entered the password correctly the first time.
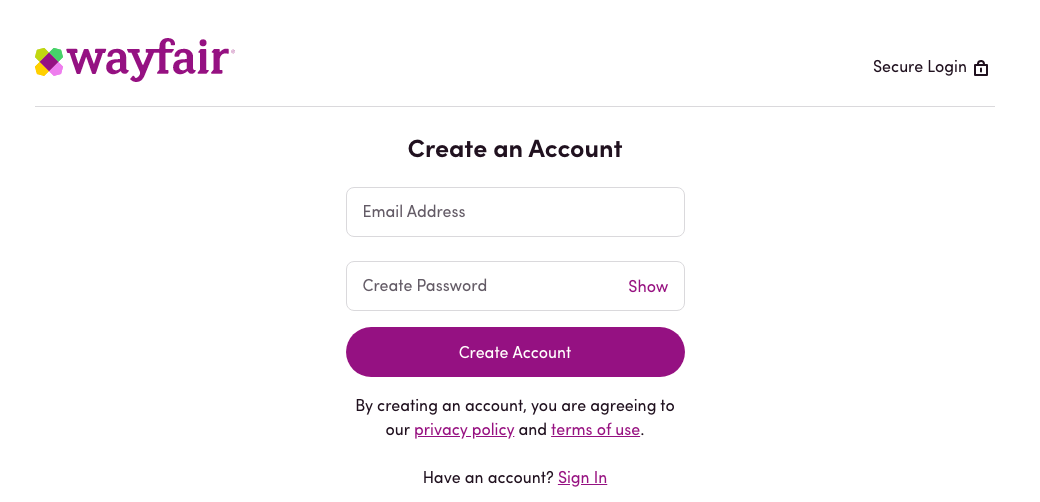
This may not sound like a significant obstacle. However, it may force website visitors to leave the page. Thus, you should either simplify the registration process or allow customers to purchase products without registering, which makes the purchasing process even easier.
Missing placeholder text
Placeholder text is text in an input field that shows an example of the expected data format. It helps a user understand what information they need to enter in a certain field and in what exact format. Add placeholder text in fields that require data in a particular format and are likely to cause difficulties. For instance, order numbers for tracking. Don’t add a placeholder in fields where the input can be intuitively understood, however, as it’s excessive.
No field masking
Field masking is used to format input text. For instance, if a user inputs 16 digits of a credit card number, field masking can divide the input into four sections with four digits each so it’s easier for the user to make sure the card number is entered correctly. If field masking is not used, the credit card number will look like a single line with 16 digits, which makes it less convenient to check.
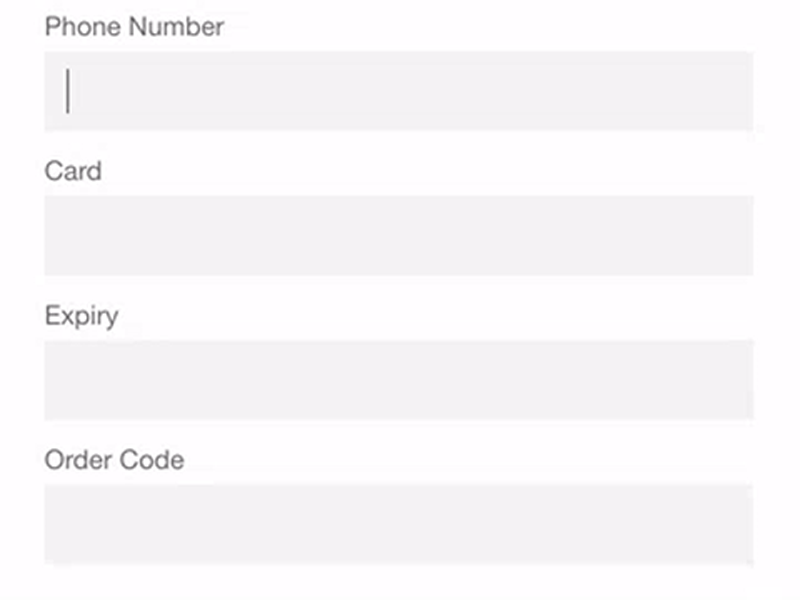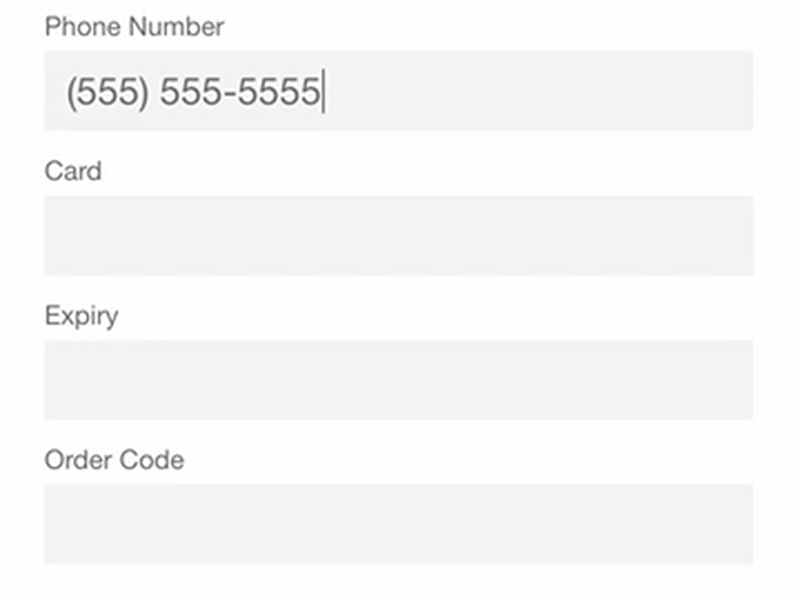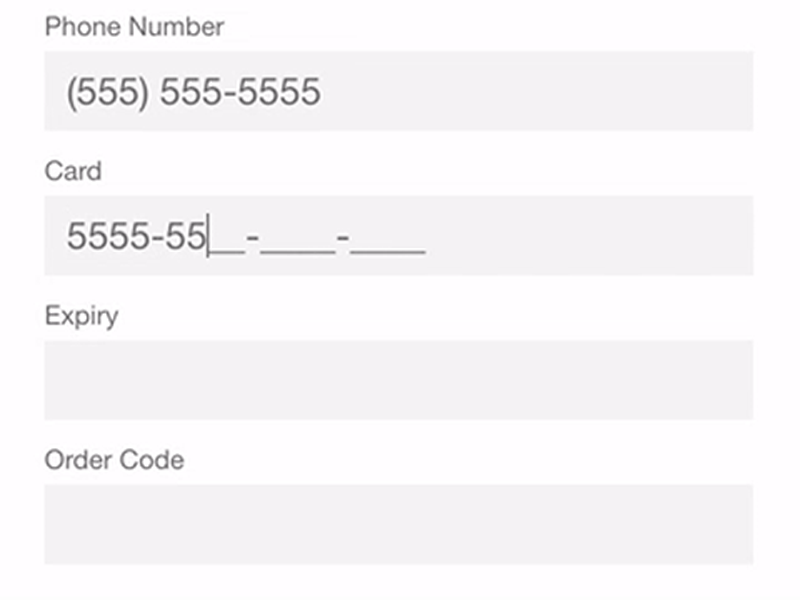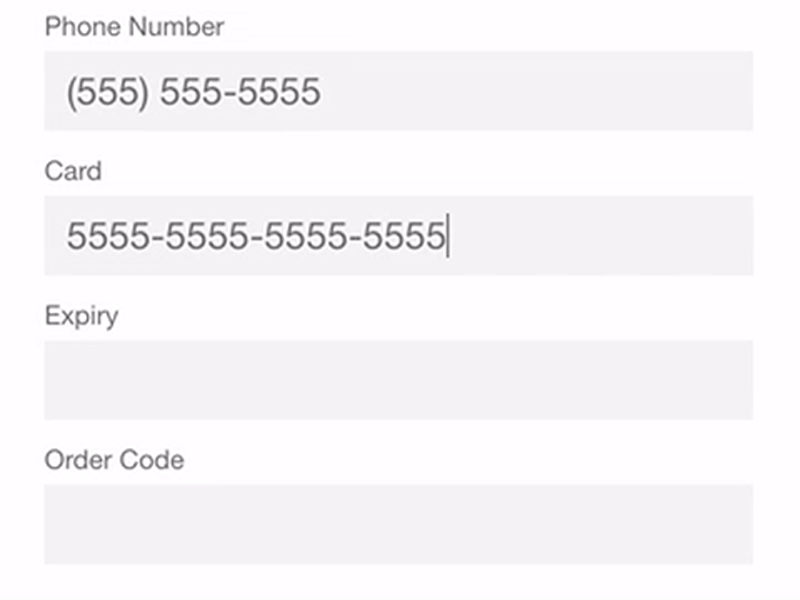
Needing to enter both billing and shipping addresses
It can be time-consuming and irritating for a customer to enter two addresses. In most cases, the billing and shipping addresses are the same unless an item is a gift. Thus, it’s best to prefill the billing address with the shipping address.
#2 Pages without navigation
After wandering through your website’s pages, a user may not be able to figure out how to return to the home page. This may lead to confusion and force the user to leave your website. Make sure that each of your website pages has clear navigation – or at least a go back button.
Ecommerce websites usually have a large number of items arranged in a hierarchical manner. Breadcrumbs can be used on ecommerce websites to improve navigation. This navigational tool reveals the user’s location on the website within nested categories. Here’s how breadcrumbs are implemented on Amazon.
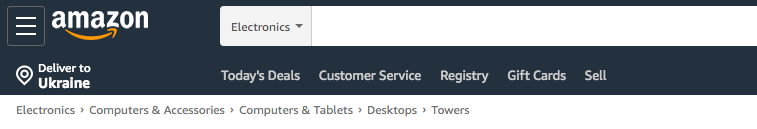
#3 Issues with the shopping cart
No way to change the number of items directly in the cart
What can be more irritating than needing to go to another page to edit the number of items you wish to purchase? Use inline editing in your website’s cart or at least provide a quick look feature on the cart page so customers don’t need to navigate to product pages in order to change item quantities.
No notification when an item is added to the cart
When users add an item to the cart and nothing is shown, it makes them guess if the item was really added. This causes them either to add the same item to the cart again or go to the cart to check if the item is already there. To avoid redundant actions, add a message each time an item is added to the cart.
Complicated process of removing an item
The ability to delete an item from the cart is also vital. Don’t use the X sign for removing items. It’s more convenient for customers if you use a remove button instead. Moreover, it would be great if the customer could remove an item from the cart by entering a 0 quantity. Remember that users don’t always press remove buttons intentionally. Instead of removing the item immediately, ask for confirmation in a pop-up notification.
#4 Issues with product pages
Item availability isn’t mentioned
Trying to buy an item that’s out of stock can be frustrating. Let users know if an item is available on the product page or simply hide items that are sold out.
No wishlist option
Some users won’t purchase your products right away. For instance, they might not buy if they’re comparing several items from one category or if they want to check out the product on your competitor’s website. That’s why they need an option to save an item for later.
Usability testing is the solution
All the issues we’ve described can be solved with usability testing. This type of testing aims at detecting bottlenecks and inconveniences a customer may have while using your ecommerce website. Let’s take a look at some other types of testing you need to apply to your website and issues they can solve.
Types of testing and problems they solve for your ecommerce website
Functional testing
This type of testing helps you analyze if the application is consistent with the product’s functional requirements and specifications. This type of testing allows you to observe how processes are performed by giving a system a certain input and analyzing the output.
Functional testing of an ecommerce website includes the following steps:
- Identifying the system’s functionality.
- Establishing the proper input according to the system’s expectations.
- Identifying the corresponding output expected from the system.
- Conducting a test.
- Comparing the expected results with the real results.
Functional testing helps you check if all application components perform properly. For example, you can check if an item is added to the cart after clicking the add to cart button or if the correct results are shown when performing a search.
Usability testing
This type of testing aims at evaluating the user-friendliness of your website and helps you detect issues users face while using it. There are various techniques for usability testing. Here we will review the most common methods experienced QA teams use to test ecommerce websites.
Hallway usability testing
This is a testing technique according to which random users conduct testing instead of experienced testing specialists. During a hallway usability test, users perform actions typical of real users such as adding an item to the cart, searching for a specific item, making an order, filtering search results, etc. This technique aims at defining usability issues on the website and collecting feedback about the user experience.
Expert review
Experienced QA engineers perform this analysis, which gives you the possibility to view your application from different perspectives. QA engineers will use the website like an ordinary user would and also run test cases to check the website’s limits. QA engineers have rich experience and know the way software should work, allowing them to view issues from a technical point of view.
Security testing
Security is one of the essential components in ecommerce. Security testing allows engineers to check if all application components are sufficiently protected. Efficient security testing allows for identifying vulnerabilities, preventing security issues such as data breaches, keeping software immune to cyber attacks, and avoiding financial risks.
Performance testing
Performance is crucial for an ecommerce website. It influences your customers’ impression of your store. If the performance is poor, you can hardly receive high sales. Performance testing allows engineers to detect components of the system that slow down the performance of the entire application. Thus, you have a chance to fix performance issues before the release.
Database testing
When developing an ecommerce application, it’s critical to ensure that the database works properly. Database testing helps you check the schema, tables, and other database constituents by creating complicated load requests and stressing the database to evaluate its responsiveness. Database testing also identifies if the following requirements have been satisfied:
- All data entered by the customer is saved in the database and displayed correctly.
- No data is lost when performing a query.
- Data entered during a process that was canceled isn’t saved in the database.
- A user’s personal data isn’t available to others.
Mobile, cross-platform, and cross-browser testing
Your website visitors may access your website from a wide range of devices, and the look of your site may differ on all of them. To provide an exceptional user experience to each of your website visitors, you should test the way your website works on different devices, platforms, and browsers. Several testing approaches are used to accomplish this.
Mobile application testing
Mobile application testing is used for testing the mobile version of your application to check its usability, consistency, and compatibility with requirements.
Cross-platform testing
This approach focuses on how your application works in different environments (for instance, on different operating systems or different software versions) to identify things that need to be improved.
Cross-browser testing
The same web page may look different on different browsers. Sometimes, the difference is slight and hard to notice; however, in some cases, the difference may be considerable and even spoil the way the website looks. Cross-browser testing aims at identifying such issues.
Recap
We’ve reviewed the major types of ecommerce website testing. Each is used to analyze an ecommerce application from a different perspective. Using all these kinds of testing allows you to detect your application’s drawbacks and eradicate them to provide your clients with the best customer experience.
Challenges of ecommerce testing
Let’s review the challenges you may face while testing your ecommerce website.
#1 Changing regulations and stricter norms
In the first half of 2019, data breaches exposed 4.1 billion records, and the number of reported breaches was 54% higher than in the first half of 2018. International organizations try to decrease the number of cyber attacks and protect internet users’ data from being stolen by making data protection laws stricter.
The task of an ecommerce website owner is to define where goods are distributed and get acquainted with the applicable laws and regulations. Examples of such regulations are the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the European Economic Area, the Federal Trade Commission Act in the United States, and the Good Practice Guide (GPG13) in the United Kingdom. Failure to comply with these and other regulations may result in huge penalties for ecommerce website owners.
#2 Poor testing strategy
The wrong testing approach and a lack of testing experience may lead to such issues as release delays, customer complaints, security issues, and, consequently, monetary losses. To run application testing effectively, a QA team should use proper approaches and follow established algorithms. If you don’t have people with enough testing experience on your team, you can hire an external testing team to ensure your product works flawlessly.
#3 Miscommunication when working with an external QA team
If you decide to hire an external QA team, you need to look for the best fit. Misunderstandings between the owner of an ecommerce website and an external QA team may cause frustration, failed expectations, and wasted time and money. Experienced vendors check a customer’s expectations for the testing process as well as all technical and business requirements to set the proper tasks. One efficient way to elicit all requirements and create a clear view of what should be achieved during testing is to clarify the following aspects:
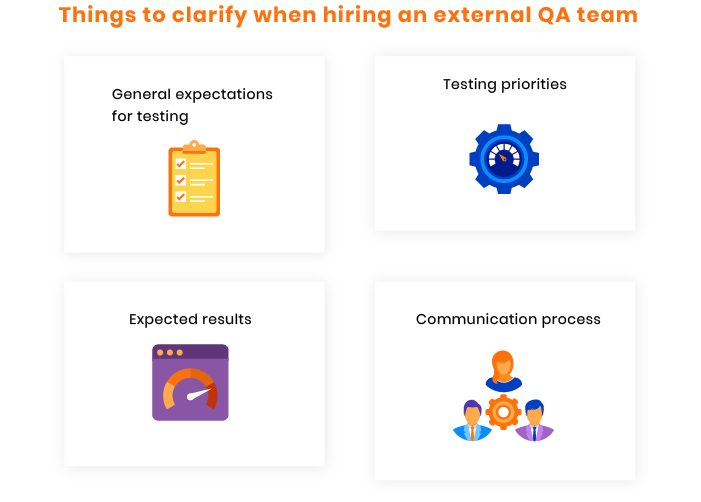
#4 Treating testing as a one-time process
Like development, testing is continuous. Each time your web application is updated, you need to run a series of tests to make sure the update doesn’t affect existing functionality and performance, trigger usability issues, or introduce security threats.
Manual vs. automation testing: The best approach to test your ecommerce website
Let’s review two significant types of testing to see the difference between them.
Manual testing
In this testing approach, test cases are executed manually by QA engineers. Such an approach helps to test software from the end user’s perspective and see if the application corresponds to the requirements. This type of testing aims at detecting deviations from expected behavior and reporting them to developers.
Automation testing
This testing technique involves running test cases with the help of written test scripts or automation testing tools. It’s used to automate repetitive tests and other tasks that are too complicated to perform manually. This type of testing is considered more reliable when completing tasks that require numerous repetitions.
Combining both manual and automation testing allows you to take the best from these two approaches, testing all the components of an ecommerce application thoroughly and delivering better quality testing.
Tools to test ecommerce websites
Experienced QA teams use a bunch of testing instruments to provide high-quality results and save time. We’ll review some of the tools that our team uses to test ecommerce products.
Apache JMeter
JMeter is a powerful testing tool for analyzing and measuring the performance of various applications. It gives you the possibility to generate a heavy load against an application, check database server performance, create new tests, and use plugins to visualize test results.
Browserstack
This cloud testing platform allows you to test web and mobile applications across the most on-demand browsers, operating systems, and mobile devices. It doesn’t require the installation of virtual machines, devices, or emulators.
Postman
Postman is a tool for testing application programming interfaces (APIs). It allows you to create collections of API calls to share them or run many at once calls instead of running them separately. With Postman, testing engineers can speed up the testing process and make it more efficient.
Wrapping up
Testing ecommerce websites differs significantly from testing other types of software, and not every team is aware of the aspects they should pay attention to while performing it. The points we’ve reviewed in this article give you a clear understanding of what types of testing should be used and what aspects need to be taken into consideration to make your ecommerce website responsive, secure, and user-friendly.
FAQ
-
- Increasing strictness of laws and norms
- Poor testing strategy
- Miscommunication with external QA team
- Failure to understand that testing is an ongoing process
-
Comprehensive testing of an ecommerce website includes functional, usability, security, performance, mobile, and cross-browser testing. RubyGarage offers all these testing services and more to make sure your ecommerce website is flawless.
-
Manual testing doesn’t require any tools and allows you to check the design and functionality of a website. Automation testing requires tools and can tell you if your program performs as expected. Discover the full list of pros and cons of manual and automation testing and how to choose between them.
-
- No show password button
- No placeholder text
- No field masking
- Requiring both shipping and billing address
- Pages without navigation
- Inability to edit item quantities in the cart
- Missing notifications when an item is added to the cart
- Complicated process of removing an item from the cart
- No wishlist option










