Technology Matters
Top software development and consulting company in Europe
We build solutions for startups and established businesses.
Tell us about your projectA technology partnership with RubyGarage goes beyond your immediate project
We partner with enterprises, startups, and startup accelerators. Our approach is highly collaborative, and we think about the long game from the start. We mainly focus on enterprise software development and startup development. The results of our work lay the foundation for long-term alliances.
Enterprises
For enterprise organizations, we design and develop solutions for displaying, manipulating, and storing large amounts of data. We build software that automates business processes.
Accelerators
Startup accelerators turn to us for our highly qualified specialists. We provide dedicated teams with the skills needed to accelerate the growth of innovative companies.
Startups
From pre-MVP to idea validation, we help startups develop their ideas into products and turn those products into viable businesses. With RubyGarage, you quickly get your app into users' hands.
Our case studies
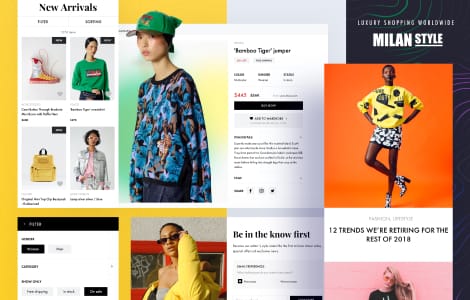
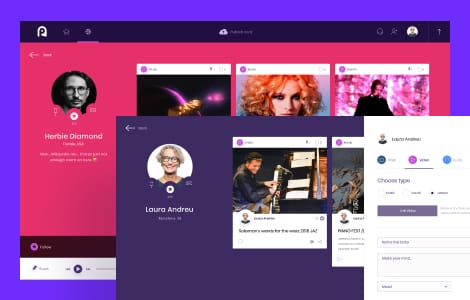
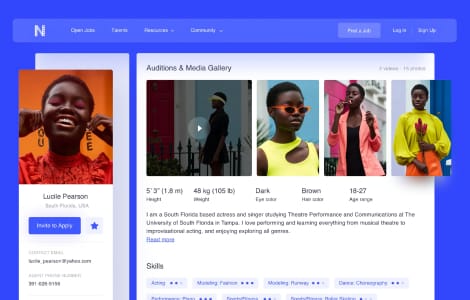
We excel at software engineering
We build products that are easy to maintain and extend. Our engineering team follows a provenwork process and maintains a consistent output of high-quality work.


Our company
RubyGarage is headquartered in Tallinn, Estonia. We have been on the market since 2011. At present, our team includes more than 100 specialists including software engineers, UI/UX designers, project managers, business analysts, quality assurance specialists, and more. We help businesses across the globe create web and mobile applications.
Trusted by entrepreneurs in many fields
Over the years, we've been accumulating our expertise in building software for different segments. Below are four industries where we have particularly strong knowledge.

Fintech
Automate, scale, secure your financial business or launch innovative Fintech products with our help.

Edutech
Cut paperwork, lower operating costs, and expand yout market with a custom e-learning platform.

E-commerce
Streamline and scale your e-commerce business with a custom platform tailored to your product segments.

Telehealth
Upgrade your workflow, enter e-health market, and increase marketability with the right custom software.
Our clients say
Quality, Dedication, Skill, Inovation, Awareness, Communication, Infrastructure, Support and Documentation” are the 9 reference-points I include in every hour per price. No other company in the world are even close to the numbers RubyGarage represents. They are simply the best.
Quite simply, I can't give the RubyGarage team high enough praise. Whatever I may manage to scribble down will totally fail to represent my admiration of their abilities. They not only revived my existing application but also provided maintenance services to ensure its proper operation.
RubyGarage exceeded my expectations in many ways. As a first time, non-technical startup founder, I am happy to say that we had a drama-free collaboration. Their leadership and project managers are experienced and pragmatic; they understand startups and offered many helpful business suggestions. Their UX designer was superb and took my product vision to a completely new level. Their dedicated team of developers delivered a quality product on time and went out of their way to delight me as a customer.
The team at RubyGarage has played a critical role in the development of our analytics platform. Our work with them is based on a strong partnership, far more valuable than a traditional offshore development relationship. Their work is of an exceptionally high standard and the whole team regularly goes the extra mile to support our business. Whatever the challenge, be it technical or operational, RubyGarage have always delivered on time and on budget.
Interested in our services?
Our Advantages
Free & non-binding offer
13+ years in the development and service design market
160+ released projects
150+ In-house specialists
Needs analysis instead of sales talk
Valuable suggestions from experts in the field for your project


